When it comes to welding, two of the most common methods you’ll encounter are MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding. Both techniques are essential in various industries, but they have distinct differences that make each one suitable for specific applications. Understanding these differences is crucial whether you’re a professional welder, a hobbyist, or someone considering a career in welding.
Overview of MIG Welding
1. What is MIG Welding?
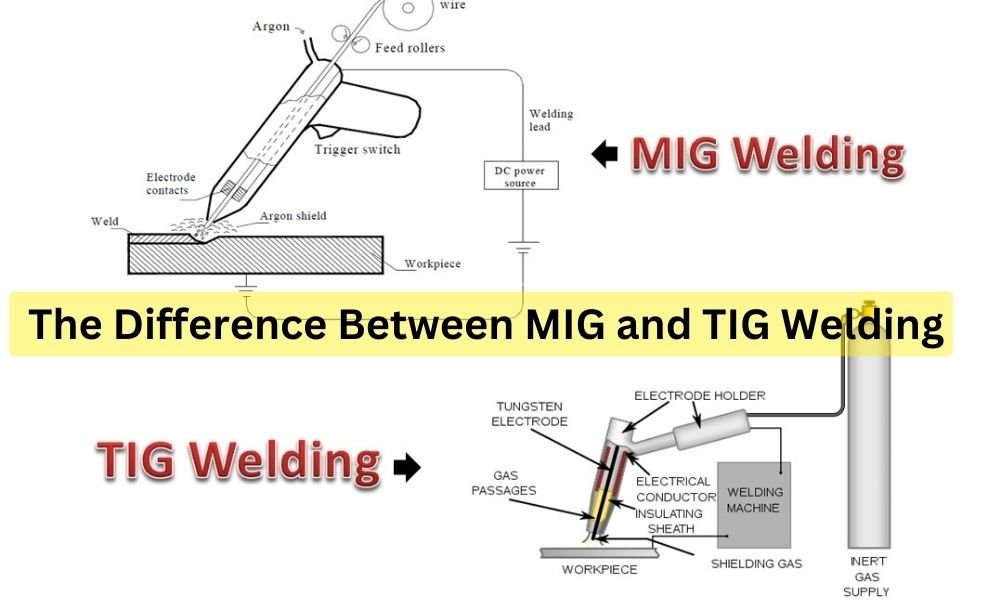
MIG welding, or Metal Inert Gas welding, involves using a continuously fed wire electrode and a shielding gas to protect the weld pool from contamination. This method is also known as GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding).
2. How MIG Welding Works
In MIG welding, the wire electrode is fed through a welding gun and melts upon contact with the weld pool, creating a strong joint between the base materials. The shielding gas, typically argon or a mixture of argon and CO2, prevents atmospheric gases from contaminating the weld.
3. Key Components of MIG Welding Equipment
- Welding Gun: The tool that feeds the wire electrode and emits the shielding gas.
- Wire Feeder: A device that continuously supplies the wire electrode to the welding gun.
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary electrical current to melt the wire electrode.
- Shielding Gas: Protects the weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
Advantages of MIG Welding
1. Speed and Efficiency
MIG welding is known for its speed, making it ideal for high-production environments. The continuous wire feed allows for faster welding compared to other methods.
2. Ease of Use
MIG welding is relatively easy to learn, making it accessible to beginners. The process is semi-automatic, which reduces the manual dexterity required.
3. Versatility in Materials
MIG welding can be used on a wide range of materials, including steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, making it a versatile choice for various applications.
Disadvantages of MIG Welding
1. Limitations with Certain Materials
While MIG welding is versatile, it struggles with welding thicker materials and metals like magnesium or titanium.
2. Portability Issues
MIG welding equipment can be bulky and less portable, limiting its use in fieldwork or remote locations.
3. Cost Considerations
The initial setup and operational costs of MIG welding can be higher due to the need for shielding gas and consumable wire electrodes.
Applications of MIG Welding
1. Industrial Uses
MIG welding is widely used in industries such as manufacturing and construction due to its efficiency and ability to handle large-scale projects.
2. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, MIG welding is commonly used for body repairs and assembly because of its speed and reliability.
3. Home and Hobby Projects
Hobbyists and DIY enthusiasts often use MIG welding for projects around the home, such as fabricating custom metal furniture or repairing machinery.
Overview of TIG Welding
1. What is TIG Welding?
TIG welding, or Tungsten Inert Gas welding, uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. This method is also known as GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding).
2. How TIG Welding Works
In TIG welding, an arc is formed between the tungsten electrode and the base material, melting the workpiece and creating a weld. A filler rod is often manually fed into the weld pool to add material.
3. Key Components of TIG Welding Equipment
- TIG Torch: Holds the tungsten electrode and emits the shielding gas.
- Power Supply: Provides the electrical current necessary for welding.
- Filler Rod: Added manually to the weld pool to create a strong joint.
- Shielding Gas: Typically argon, protects the weld area from contamination.
Advantages of TIG Welding
1. Precision and Control
TIG welding offers unparalleled control, allowing for precise and clean welds, making it ideal for detailed work.
2. Superior Weld Quality
The welds produced by TIG welding are high-quality and aesthetically pleasing, often requiring little to no finishing work.
3. Flexibility with Materials
TIG welding can be used on a variety of materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, and exotic metals like titanium.
Disadvantages of TIG Welding
1. Complexity and Skill Requirements
TIG welding is more complex and requires a higher skill level, making it challenging for beginners to master.
2. Speed Limitations
The process of TIG welding is slower compared to MIG welding, which can be a drawback in high-production environments.
3. Equipment Cost
TIG welding equipment tends to be more expensive, and the process itself can be more time-consuming and costly.
Applications of TIG Welding
1. Aerospace Industry
TIG welding is widely used in the aerospace industry for its precision and ability to produce high-quality welds on critical components.
2. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, TIG welding is used for specialized tasks such as welding stainless steel exhaust systems and custom fabrications.
3. Art and Sculpture
Artists and sculptors often use TIG welding to create intricate metal artworks due to the control and precision it offers.
Comparative Analysis
1. Skill Level Required
MIG welding is easier to learn and more forgiving, making it suitable for beginners. TIG welding, on the other hand, requires more skill and practice to achieve high-quality results.
2. Speed of Welding
MIG welding is faster and more efficient, which is beneficial for high-production environments. TIG welding is slower but offers superior precision and control.
3. Quality of Welds
While MIG welding produces strong welds, TIG welding excels in creating clean, precise, and aesthetically pleasing welds.
Material Compatibility
1. Metals Suited for MIG Welding
MIG welding is effective on various metals, including steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
2. Metals Suited for TIG Welding
TIG welding is suitable for a broader range of metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, and other exotic metals.
Cost Comparison
1. Equipment Costs
MIG welding equipment is generally less expensive than TIG welding equipment, making it more accessible for hobbyists and small businesses.
2. Operational Costs
MIG welding can be costlier in the long run due to the continuous use of consumables like wire and shielding gas. TIG welding, while initially more expensive, may have lower ongoing costs.
Safety Considerations
1. Safety Equipment for MIG Welding
MIG welding requires safety gear such as welding helmets, gloves, and protective clothing to prevent burns and exposure to harmful UV light.
2. Safety Equipment for TIG Welding
Similar to MIG welding, TIG welding also requires protective gear, with an added emphasis on precision gloves to handle the filler rod.
3. Common Safety Hazards
Both MIG and TIG welding pose risks such as burns, eye damage, and inhalation of harmful fumes. Proper ventilation and protective gear are essential for safe operation.
Which One to Choose?
1. Factors to Consider
When choosing between MIG and TIG welding, consider factors such as the materials you’ll be working with, the required precision, your skill level, and the specific needs of your projects.
2. Professional vs. Hobbyist Needs
Professionals may prefer TIG welding for its precision and quality, while hobbyists and beginners might find MIG welding more accessible and easier to learn.
Conclusion
Both MIG and TIG welding have their unique advantages and disadvantages. MIG welding is faster and easier to learn, making it suitable for high-production environments and beginners. TIG welding, while more complex, offers superior precision and weld quality, ideal for detailed and high-quality work. Ultimately, the choice between MIG and TIG welding depends on your specific needs, skill level, and the materials you’ll be working with.
FAQs
What is easier for beginners, MIG or TIG welding?
MIG welding is generally easier for beginners due to its simpler process and forgiving nature.
Can you use the same gas for MIG and TIG welding?
While argon can be used for both, MIG welding often uses a mixture of argon and CO2, whereas TIG welding typically uses pure argon.
What metals cannot be welded with MIG?
MIG welding struggles with metals like magnesium and titanium, which are better suited for TIG welding.
How long does it take to learn TIG welding?
Learning TIG welding can take several months to years, depending on the complexity of the projects and the learner’s dedication.
Is TIG welding stronger than MIG welding?
TIG welding can produce stronger and higher-quality welds, especially on thin or delicate materials, due to its precision and control.